| comments | edit_url |
|---|---|
true |
给定一个二叉搜索树,请将它的每个节点的值替换成树中大于或者等于该节点值的所有节点值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
- 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
- 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
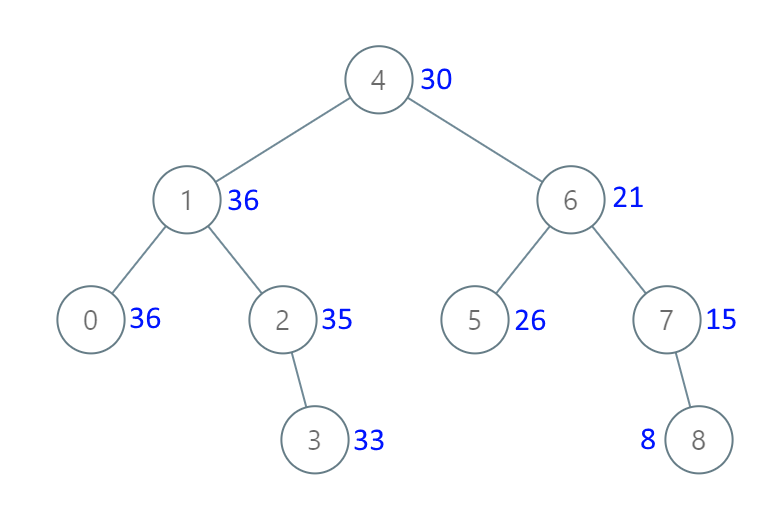
输入:root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8] 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0,null,1] 输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,0,2] 输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:
输入:root = [3,2,4,1] 输出:[7,9,4,10]
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于
0和104之间。 - 每个节点的值介于
-104和104之间。 - 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
- 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
注意:
- 本题与主站 538 题相同: https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
- 本题与主站 1038 题相同:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
按照“右根左”的顺序,递归遍历二叉搜索树,累加遍历到的所有节点值到 node 节点。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def dfs(root):
nonlocal s
if root is None:
return
dfs(root.right)
s += root.val
root.val = s
dfs(root.left)
s = 0
dfs(root)
return root/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int s;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.right);
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
dfs(root.left);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int s = 0;
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
dfs(root->right);
s += root->val;
root->val = s;
dfs(root->left);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
s := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Right)
s += root.Val
root.Val = s
dfs(root.Left)
}
dfs(root)
return root
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function convertBST(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
let sum = 0;
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null) => {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.right);
root.val += sum;
sum = root.val;
dfs(root.left);
};
dfs(root);
return root;
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, sum: &mut i32) {
if let Some(node) = root {
Self::dfs(&node.borrow().right, sum);
node.borrow_mut().val += *sum;
*sum = node.borrow().val;
Self::dfs(&node.borrow().left, sum);
}
}
pub fn convert_bst(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
Self::dfs(&root, &mut 0);
root
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var convertBST = function (root) {
let s = 0;
function dfs(root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root.right);
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
dfs(root.left);
}
dfs(root);
return root;
};/* class TreeNode {
* var val: Int
* var left: TreeNode?
* var right: TreeNode?
* init() {
* self.val = 0
* self.left = nil
* self.right = nil
* }
* init(_ val: Int) {
* self.val = val
* self.left = nil
* self.right = nil
* }
* init(_ val: Int, _ left: TreeNode?, _ right: TreeNode?) {
* self.val = val
* self.left = left
* self.right = right
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private var s = 0
func convertBST(_ root: TreeNode?) -> TreeNode? {
dfs(root)
return root
}
private func dfs(_ root: TreeNode?) {
guard let node = root else {
return
}
dfs(node.right)
s += node.val
node.val = s
dfs(node.left)
}
}Morris 遍历无需使用栈,时间复杂度
定义 s 表示二叉搜索树节点值累加和。遍历二叉树节点:
- 若当前节点 root 的右子树为空,将当前节点值添加至 s 中,更新当前节点值为 s,并将当前节点更新为
root.left。 - 若当前节点 root 的右子树不为空,找到右子树的最左节点 next(也即是 root 节点在中序遍历下的后继节点):
- 若后继节点 next 的左子树为空,将后继节点的左子树指向当前节点 root,并将当前节点更新为
root.right。 - 若后继节点 next 的左子树不为空,将当前节点值添加 s 中,更新当前节点值为 s,然后将后继节点左子树指向空(即解除 next 与 root 的指向关系),并将当前节点更新为
root.left。
- 若后继节点 next 的左子树为空,将后继节点的左子树指向当前节点 root,并将当前节点更新为
- 循环以上步骤,直至二叉树节点为空,遍历结束。
- 最后返回二叉搜索树根节点即可。
Morris 反序中序遍历跟 Morris 中序遍历思路一致,只是将中序遍历的“左根右”变为“右根左”。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
s = 0
node = root
while root:
if root.right is None:
s += root.val
root.val = s
root = root.left
else:
next = root.right
while next.left and next.left != root:
next = next.left
if next.left is None:
next.left = root
root = root.right
else:
s += root.val
root.val = s
next.left = None
root = root.left
return node/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
int s = 0;
TreeNode node = root;
while (root != null) {
if (root.right == null) {
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
root = root.left;
} else {
TreeNode next = root.right;
while (next.left != null && next.left != root) {
next = next.left;
}
if (next.left == null) {
next.left = root;
root = root.right;
} else {
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
next.left = null;
root = root.left;
}
}
}
return node;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
int s = 0;
TreeNode* node = root;
while (root) {
if (root->right == nullptr) {
s += root->val;
root->val = s;
root = root->left;
} else {
TreeNode* next = root->right;
while (next->left && next->left != root) {
next = next->left;
}
if (next->left == nullptr) {
next->left = root;
root = root->right;
} else {
s += root->val;
root->val = s;
next->left = nullptr;
root = root->left;
}
}
}
return node;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
s := 0
node := root
for root != nil {
if root.Right == nil {
s += root.Val
root.Val = s
root = root.Left
} else {
next := root.Right
for next.Left != nil && next.Left != root {
next = next.Left
}
if next.Left == nil {
next.Left = root
root = root.Right
} else {
s += root.Val
root.Val = s
next.Left = nil
root = root.Left
}
}
}
return node
}