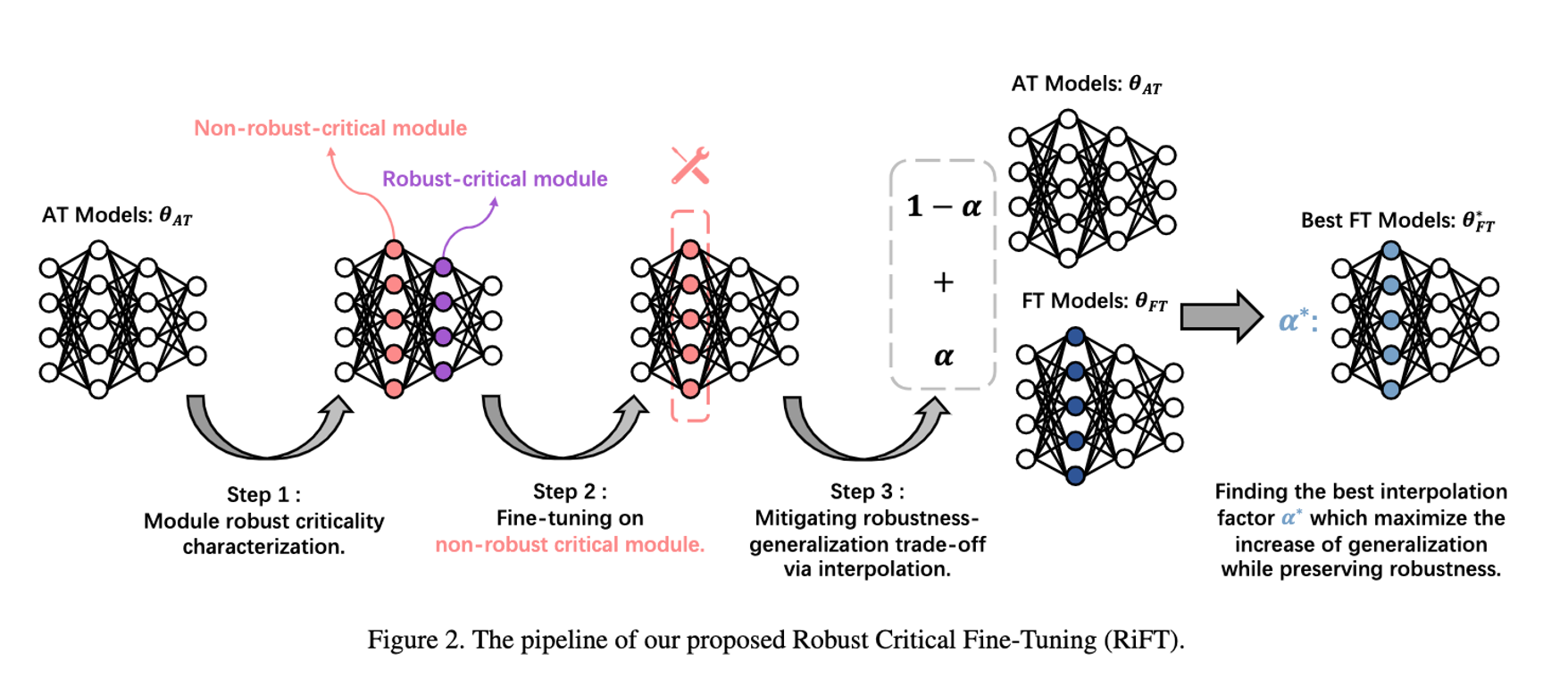
This is the official implementation of ICCV2023 Improving Generalization of Adversarial Training via Robust Critical Fine-Tuning.
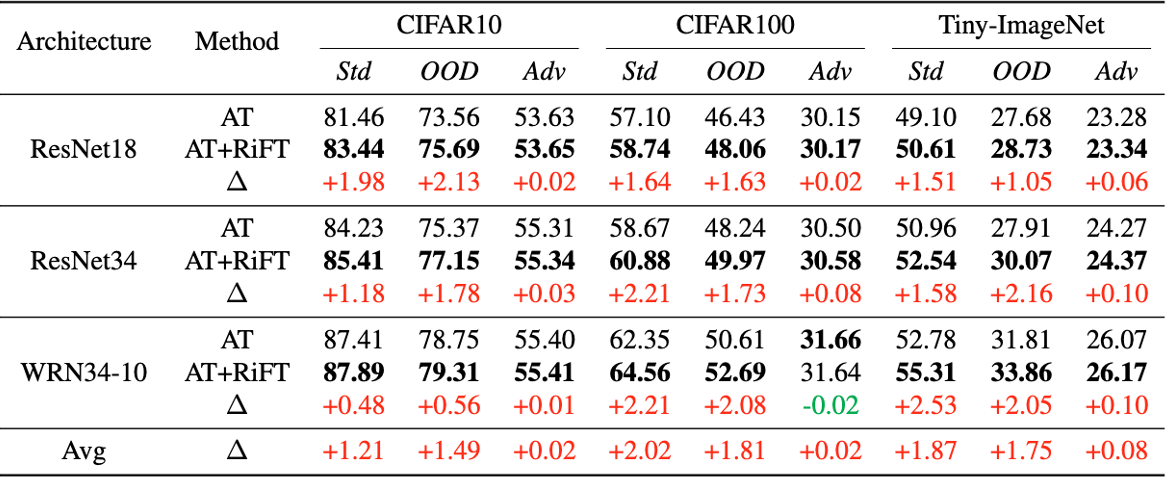
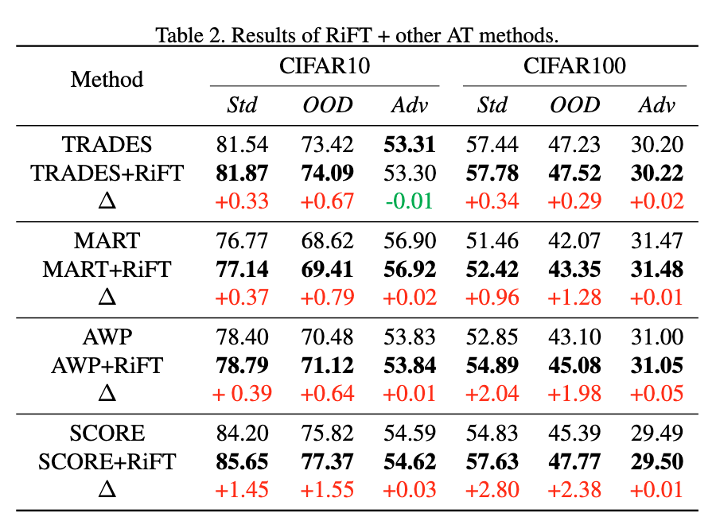
Abstract: Deep neural networks are susceptible to adversarial examples, posing a significant security risk in critical applications. Adversarial Training (AT) is a well-established technique to enhance adversarial robustness, but it often comes at the cost of decreased generalization ability. This paper proposes Robustness Critical Fine-Tuning (RiFT), a novel approach to enhance generalization without compromising adversarial robustness. The core idea of RiFT is to exploit the redundant capacity for robustness by fine-tuning the adversarially trained model on its non-robust-critical module. To do so, we introduce module robust criticality (MRC), a measure that evaluates the significance of a given module to model robustness under worst-case weight perturbations. Using this measure, we identify the module with the lowest MRC value as the non-robust-critical module and fine-tune its weights to obtain fine-tuned weights. Subsequently, we linearly interpolate between the adversarially trained weights and fine-tuned weights to derive the optimal fine-tuned model weights. We demonstrate the efficacy of RiFT on ResNet18, ResNet34, and WideResNet34-10 models trained on CIFAR10, CIFAR100, and Tiny-ImageNet datasets. Our experiments show that RiFT can significantly improve both generalization and out-of-distribution robust- ness by around 1.5% while maintaining or even slightly enhancing adversarial robustness. Code is available at https://github.com/microsoft/robustlearn.
To install requirements:
conda env create -f env.yaml
conda activate rift
CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 can be downloaded via PyTorch.
For other datasets:
After downloading these datasets, move them to ./data.
The images in Tiny-ImageNet datasets are 64x64 with 200 classes.
Here we present a example for RiFT ResNet18 on CIFAR10.
Download the adversarially trained model weights here.
python main.py --layer=layer2.1.conv2 --resume="./ResNet18_CIFAR10.pth"
- layer: the desired layer name to fine-tune.
Here, layer2.1.conv2 is a non-robust-critical module.
The non-robust-critical module of each model on each dataset are summarized as follows:
| CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | Tiny-ImageNet | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | layer2.1.conv2 | layer2.1.conv2 | layer3.1.conv2 |
| ResNet34 | layer2.3.conv2 | layer2.3.conv2 | layer3.5.conv2 |
| WRN34-10 | block1.layer.3.conv2 | block1.layer.2.conv2 | block1.layer.2.conv2 |
- Characterize the MRC for each module
python main.py --cal_mrc --resume=/path/to/your/modelThis will output the MRC for each module. - Fine-tuning on non-robust-critical module
Based on the MRC output, choose a module with lowest MRC value to fine-tune.
We suggest to choose the middle layers according to our experience.
Try different learning rate! Usually a small learning rate is preferred.
python main.py --layer=xxx --lr=yyy --resume=zzzWhen fine-tuning finish, it will automatically interpolate between adversarially trained weights and fine-tuned weights. The robust accuracy, in-distribution test acc are evaluated during the interpolation procedure. - Test OOD performance. Pick he best interpolation factor (the one with max IID generalization increase while not drop robustness so much.)
python eval_ood.py --resume=xxx
- Kaijie Zhu: [email protected]
- Jindong Wang: [email protected]
@inproceedings{zhu2023improving,
title={Improving Generalization of Adversarial Training via Robust Critical Fine-Tuning},
author={Zhu, Kaijie and Hu, Xixu and Wang, Jindong and Xie, Xing and Yang, Ge },
year={2023},
booktitle={International Conference on Computer Vision},
}