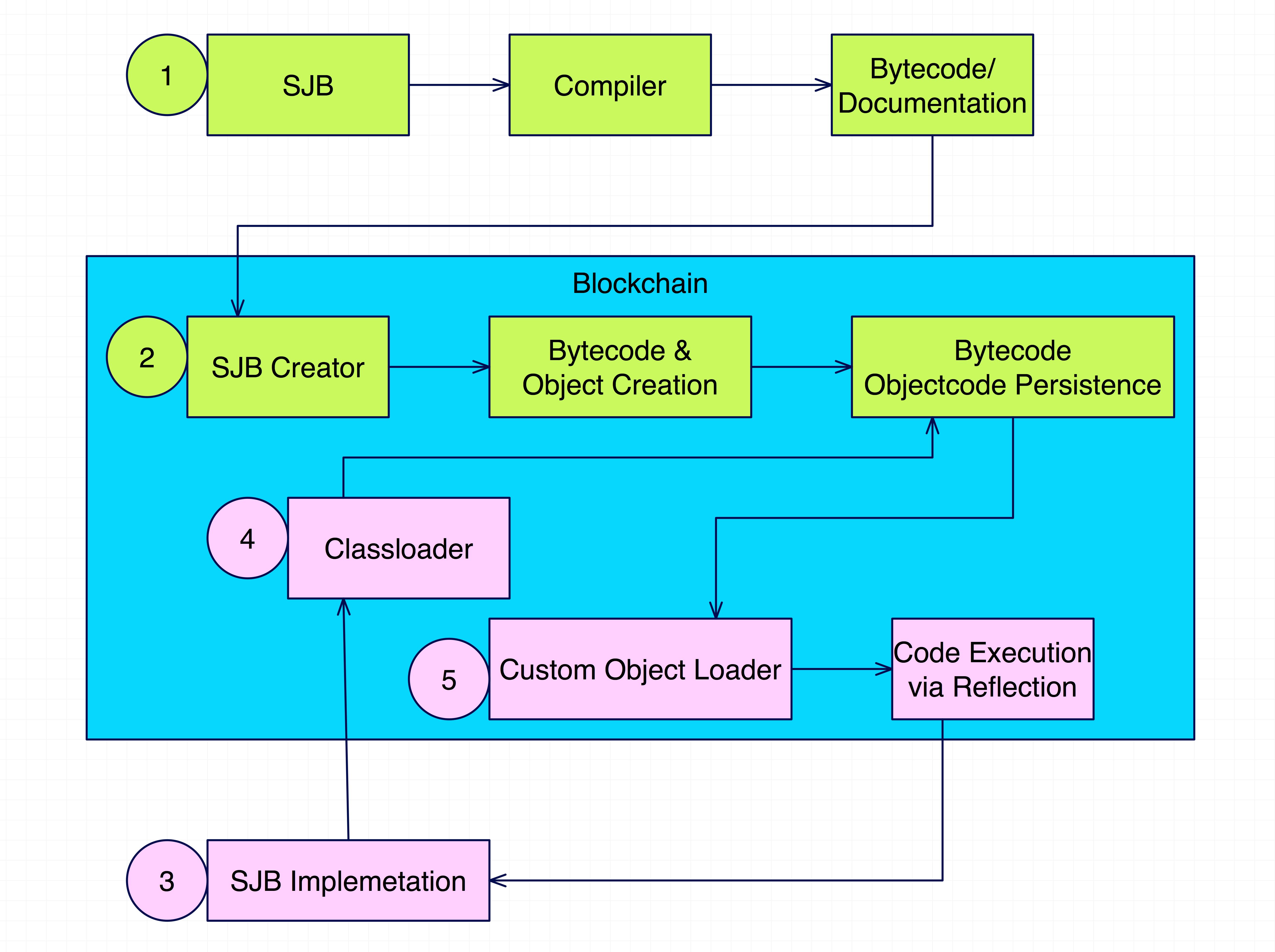
The NXT platform is a powerful blockchain platform. The only down-side is there are no smart contracts. Our aim is to be able to implement Smart Contracts on the NXT blockchain. We call these Smart Contracts Smart Java Beans (or SJB for short).
- SJBs are normal java beans that can be run on the NXT blockchain.
- SJBs are stateful. see Stateless & Stateful Smart Contracts
- There's a helper interface called
Contract. All SJBs must implement this interface and provide implementations for all its methods. - SJBs must have access to all the APIs exposed by the NXT platform.
- SJBs must follow the below naming conventions
- Methods that must return a value MUST begin with get, e.g
public long getAccountBalance(). These types of methods cost 0 to execute and doesn't affect the state of the SJB on the blockchain - Every other method except 1. above will have side effects. i.e will cause a new state for the contract to be stored on the chain. Methods that have side effects must return void. e.g
public void setAccountBalance(int long). After the execution of this method, the state of the SJB object will be altered. - SJBs must provide a setter and getter for a variable named
version, the type ofversionis int. This is enforced by theContractinterface.
- Methods that must return a value MUST begin with get, e.g
When a get request is sent to the contract, no state is generated, therefore, we don't need to manage state. But when any other method is executed, first the node checks if it has enabled smart contract execution, next it fires up the custom class loader and object input stream, loads the class and the object and runs the method. It then also runs the method setVersion(getVersion() + 1) on the contract. Finally, a trasanction is queued to save this new state on the blockchain. However before the state is saved, it checks that [IncomingSmartContractState].getVersion() is equal to [SmartContractCurrentlyOnBlockchain].getVersion() + 1. If this condition is true, the new state is saved.
We need a custom dynamic class loader, that could load classes into memory from bytecode. We also need a custom ObjectInputStream that can use the Dynamic class loader. All these is put together in this project InMemoryJavaCompiler to compile java source file into bytecode. After compilation, the InMemory compiler returns the bytecode and a documentation (json) generated from the source file (sample included below)
After compilation, the bytecode and documentation are sent in an API call to the blockchain. The API will store us the Dynamic Class Loader to load the bytecode, then an instance is created. The Custom ObjectInputStream is used to serialize the instance. A base64 encoded String of both the bytecode and the serialized instance are stored in the DB along with the documentation.
The API also include a call that will return the documentation so that the developer can know the methods and return types of the methods.
When the API call to execute the smart contract is made, the Dynamic Class Loader loads the bytecode from memory, the custom ObjectInputStream loads the instance (Using the class loader) and using reflections, the proper method and variables are passed to the instance.
If the call is a set method, the new instance is serialized once again and put on the blockchain.
Nodes can set the nxt.shouldRunSmartContracts=true to run smart contracts. If it's false, the node will not process smart contracts. Apart from this, nodes can also provide a contracts.json file to specify which particular contracts to run, nodes can also specify which particular methods within the contract they want to execute.
If a contracts.json is not found, all contracts and all contracts methods will be run if nxt.shouldRunSmartContracts=true, otherwise the node will not process contracts.
{
"all": false,
"contracts": [
{
"id": "1666950666991748874",
"execute": true,
"methods": []
},
{
"id": "7241189096096398119",
"execute": true,
"methods": ["sendMoney", "getAccountBalance", "sendMessage"]
}
]
}
"documentation": {
"methods": [{
"name": "getVersion",
"parameters": [],
"returnType": "int"
}, {
"name": "registerVoter",
"parameters": ["nxt.smartcontract.api.SmartAccount"],
"returnType": "void"
}, {
"name": "getRegistered",
"parameters": [],
"returnType": "java.util.Set"
}, {
"name": "vote",
"parameters": ["nxt.smartcontract.api.SmartAccount"],
"returnType": "void"
}, {
"name": "getVoters",
"parameters": [],
"returnType": "java.util.Set"
}, {
"name": "setVersion",
"parameters": ["int"],
"returnType": "void"
}],
"name": "ng.com.idempotent.hellosmartbean.VotingBean"
}
import nxt.smartcontract.api.SmartBean;
public class SimpleSJB implements SmartBean {
int version;
@Override
public int getVersion() {
return version;
}
@Override
public void setVersion(int version) {
this.version = version;
}
}
This type of bean must extend SmartTransaction because it will perform a transaction on the blockchain.
package ng.com.idempotent.hellosmartbean;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import nxt.Account;
import nxt.Attachment;
import nxt.smartcontract.api.SmartAccount;
import nxt.smartcontract.api.SmartBean;
import nxt.smartcontract.api.blockchain.request.ParameterParser;
import nxt.smartcontract.api.blockchain.request.SmartRequest;
import nxt.smartcontract.api.blockchain.request.SmartTransaction;
import nxt.smartcontract.api.utils.Constants;
import org.json.simple.JSONStreamAware;
/**
*
* @author aardvocate
*/
public class SimpleSJB extends SmartTransaction implements SmartBean {
int version;
@Override
public int getVersion() {
return version;
}
@Override
public void setVersion(int version) {
this.version = version;
}
public String sendMoney(SmartAccount sender, SmartAccount recipient, Long amountNQT) throws Exception {
SmartRequest smartRequest = new SmartRequest(Attachment.ORDINARY_PAYMENT);
smartRequest.putParameter("recipient", recipient.getAddress());
smartRequest.putParameter("secretPhrase", sender.getPassphrase());
smartRequest.putParameter("feeNQT", Constants.ONE_NXT + "");
smartRequest.putParameter("deadline", "6");
long recipientId = ParameterParser.getAccountId(smartRequest, "recipient", false);
Account senderAccount = ParameterParser.getSenderAccount(smartRequest);
JSONStreamAware json = createTransaction(smartRequest, senderAccount, recipientId, amountNQT);
StringWriter stringWriter = new StringWriter();
json.writeJSONString(stringWriter);
return stringWriter.getBuffer().toString();
}
}
public void testPushSmartContract() throws Exception {
File f = new File("logs");
f.mkdirs();
String passphrase = "Baba fi owo kan idodo omo oni dodo ni dodo ilu wa";
SmartAccount account = new SmartAccount(passphrase);
File source = new File("/Users/aardvocate/src/HelloSmartBean/src/main/java/ng/com/idempotent/hellosmartbean", "HelloSJBWorld.java");
String className = "ng.com.idempotent.hellosmartbean.HelloSJBWorld";
String s = SmartCall.createSmartContract(account, source, className);
Assert.assertNotNull(s);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
HashMap responseMap = om.readValue(s, HashMap.class);
Assert.assertTrue(responseMap.containsKey("smartContractId"));
System.err.println(responseMap.get("smartContractId"));
}
public void testExecuteSendMoney() throws Exception {
System.out.println("testExecuteSendMoney");
//account that owns the smart contract
SmartAccount owner = new SmartAccount(1565770067262084023L);
long id = 7241189096096398119L;
//this is the account calling the smart contract. This account will bear the fees
SmartAccount executingAccount = new SmartAccount("copper explain fated truck neat unite branch educated tenuous hum decisive notice");
SmartAccount sender = new SmartAccount("Baba fi owo kan idodo omo oni dodo ni dodo ilu wa");
SmartAccount recipient = new SmartAccount(2595880067262094023L);
String fullyQualifiedClassName = "ng.com.idempotent.hellosmartbean.HelloSJBWorld";
SmartMethod smartMethod = new SmartMethod("sendMoney");
smartMethod.setParameterTypes(SmartAccount.class, SmartAccount.class, Long.class);
smartMethod.setParameterValues(sender, recipient, (100 * Constants.ONE_NXT));
SmartClass smartClass = new SmartClass(owner, id, fullyQualifiedClassName);
smartClass.setSmartMethod(smartMethod);
String result = SmartCall.executeSmartContract(smartClass, executingAccount);
HashMap resultMap = new ObjectMapper().readValue(result, HashMap.class);
assertTrue(resultMap.containsKey("transactionJSON"));
assertTrue(resultMap.containsKey("transaction"));
}
Check the src folder and test folder for more examples.